Erlang B is a traffic model which can be used to explore the relationship between the busy hour traffic offered to a trunk group, the required grade of service and the number of lines required. That makes it useful for route dimensioning (determining how many lines are required on a trunk group).
The Erlang B traffic model used by Westbay Traffic Calculators can help you work out how many lines you should install in a trunk group. You can learn the process of sizing a trunk group in our technical paper.
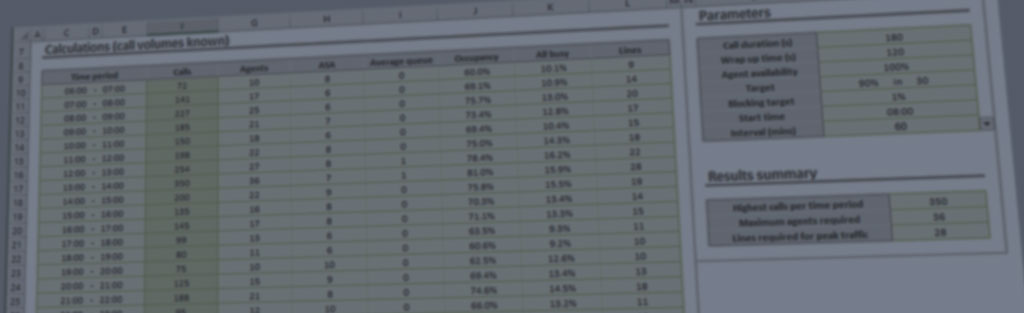
You can use the Erlang C traffic model included with Westbay Traffic Calculators to estimate how many agents you need at your inbound call center. We explain the process of call center agents calculation in our technical paper.
Yes. Wrap-up time (or wrap time) is the time your agent remains unavailable after finishing with a call, usually to complete call-related administrative tasks. As wrap-up time uses an agent’s time in the same way as actually handling a call, it should be included in the average call duration figure.
However, when using Erlang B to estimate the number of lines required into a call center to deliver inbound calls, wrap-up time should not be included, but the average delay to all calls should be included as queuing time occupies a trunk in the same way as conversation time.
You need to work out the number of hours traffic offered to a trunk group during the busiest hour. Use the following formula:
Busy Hour Traffic = Number of calls * Average call duration (s) / 3600
If possible, you should extract these figures from a call logger. Otherwise, you will need to make reasonable estimates based on your understanding of your business. Remember that the busy hour figure should represent the busiest hour you are ever likely to encounter, so use a month or two’s data to work it out.
Yes. By pressing the Results button, you can see a list of all calculations you have made during the previous week. You can filter this list so that the results on view are only for the current session, or any day during the past week. This calculation history can also be printed.
We don’t think it’s very accurate, so we do not support Poisson (or Molina). To model situations where there are a high number of retries (callers who immediately redial because they have encountered blocking) we prefer to use the Extended Erlang B traffic model because it allows you to specify the ratio of blocked calls that will immediately retry.
The Erlang B calculator works up to 90,000 lines and 90,000 Erlangs busy hour traffic. The Erlang C calculator works up to 1,000,000 calls per hour and 10,000 agents.
Our desktop products work on all versions of Windows from Vista to Windows 11. We do not make software for the Apple Mac.
Westbay Traffic Calculator costs $99 (US dollars) for an installation on a single computer. We also offer enterprise licences for multiple installations.
This is a once-only payment and includes free upgrades for the lifetime of the product.


My Westbay erlang calculator has stopped working. It produces a #name? result in my spreadsheet.
This was a known problem and was fixed in a release in August 2018. I have written to you by email with downloading instructions for the latest version. Please reply if you need any further support.